Blogs

Different Types of Dredgers: Complete Technical Guide for Modern Dredging & Shipbuilding Projects (2025)
Summary
This blog provides a comprehensive, specialist-level breakdown of the different types of dredgers used across the dredging and marine engineering sector. It explains how each dredger works, where it performs best, its operational limitations, and how project owners can match the right dredger to their seabed conditions and project scope. The goal is to help marine consultants, EPC contractors, port authorities, and offshore developers make informed decisions while positioning Rock & Reef as a solution-driven partner for dredging and shipbuilding.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Exactly Is a Dredger?
- Classification of Dredgers
- Mechanical Dredgers
- Backhoe Dredger
- Grab/Clamshell Dredger
- Bucket Ladder Dredger
- Hydraulic Dredgers
- Cutter Suction Dredger (CSD)
- Trailing Suction Hopper Dredger (TSHD)
- Plain Suction Dredger
- Special Purpose Dredgers
- Water Injection Dredger
- Amphibious Dredger
- Auger Suction Dredger
- Comparison Table: Technical & Operational Differences
- Graph: Productivity Comparison Across Major Dredger Types
- Selecting the Right Dredger for Your Project
- How Rock & Reef Delivers End-to-End Dredging & Marine Engineering Solutions
- Final Thoughts & Expert Recommendations
1. Introduction
Dredging has always been a cornerstone of maritime development. Whether it’s deepening channels, maintaining berths, reclaiming land, laying underwater pipelines, or executing trenching works, choosing the right dredger defines whether a project stays efficient, economical, and technically sound.
As a team servicing India’s marine sector, we see a common challenge: many stakeholders know the outcome they want, but not the machine that can achieve it. So this content aims to bridge that gap.
2. What Exactly Is a Dredger?
A dredger is a heavy marine machine designed to remove, excavate, or relocate underwater soil, silt, rock, or sediments. It’s engineered to perform controlled excavation in challenging hydrodynamic conditions and transport the dredged material safely to disposal or reclamation sites.
3. Classification of Dredgers
Dredgers are generally classified into:
- Mechanical Dredgers – physically dig material
- Hydraulic Dredgers – pump material through suction systems
- Special Purpose Dredgers – designed for niche or sensitive environments
4. Mechanical Dredgers
Mechanical dredgers are ideal for compact soils, localized works, or areas requiring precision.
4.1 Backhoe Dredger (BHD)
A backhoe dredger is mounted on a floating pontoon and equipped with a hydraulic arm similar to land-based excavators.
Applications:
Harbour deepening
Rock removal
Capital dredging
Pipeline trenching
Strengths:
Highly accurate
Works well in hard soil and rock
Minimal turbidity
Limitations:
Lower production than hydraulic dredgers
Not suitable for soft sediments
4.2 Grab / Clamshell Dredger
A wire-operated crane that drops a grab bucket, scoops sediment, and lifts it back.
Best for:
- Maintenance dredging
- Port berths
- Urban waterfronts
Strengths:
- Flexible in congested zones
- Good for debris and mixed material
4.3 Bucket Ladder Dredger
An older but highly effective dredger with a chain of buckets.
Strengths:
- Precise cuts
- Good for gravel and compact layers
Limitations:
- High operational complexity
5. Hydraulic Dredgers
Hydraulic dredgers use pumps, suction arms, and pipelines for continuous material transport.
5.1 Cutter Suction Dredger (CSD)
The most versatile dredger in modern marine engineering.
Applications:
- River deepening
- Channel creation
- Trenching for pipelines
- Land reclamation
Strengths:
- High production
- Handles clay, compact soil, and soft rock
- Continuous pumping to disposal
5.2 Trailing Suction Hopper Dredger (TSHD)
A self-propelled dredger that trails suction pipes along the seabed.
Best for:
- Offshore sand mining
- Port maintenance
- Long-haul dredging
Strengths:
- Fast
- Good for high-volume projects
- Hopper allows long-distance disposal
5.3 Plain Suction Dredger
No cutter head – uses pure suction.
Best for:
- Soft silt
- Fine sediments around estuaries
6. Special Purpose Dredgers
These are designed for sensitive jobs and site-specific constraints.
6.1 Water Injection Dredger (WID)
Uses low-pressure jets to fluidize sediment.
Best for:
- Maintenance dredging
- Shallow zones
- Low-cost operations
6.2 Amphibious Dredger
Works both on land and water.
Use Cases:
- Swamps
- Lakes
- Floodplains
6.3 Auger Suction Dredger
Equipped with a rotating auger for controlled cutting.
Ideal For:
- Environmental dredging
- Sensitive industrial ponds
7. Comparison Table: Technical & Operational Differences
| Dredger Type | Best Soil Type | Production Rate | Ideal Project Type | Mobility | Accuracy |
| Backhoe Dredger | Hard soil, rock | Medium | Capital works | Low | High |
| Grab Dredger | Mixed material | Medium | Berths, rivers | Medium | Medium |
| CSD | Clay, sand, soft rock | Very High | Reclamation, channels | Low | Moderate |
| TSHD | Sand, silt | High | Offshore, ports | Very High | Low |
| Plain Suction | Soft soils | Medium | Estuaries | Low | Low |
| Amphibious | Silt, clay | Low | Swamps | Medium | High |
| Auger | Soft sediments | Medium | Environmental ponds | Low | Very High |
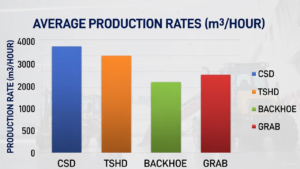
8. Graph: Productivity Comparison Across Major Dredger Types
Graph Suggestion:
A bar chart comparing average production rates (m³/hour):
- CSD
- TSHD
- Backhoe
- Grab
- Augur
9. Selecting the Right Dredger for Your Project
A practical selection framework:
- Soil Investigation Report (SIR)
– Determines soil hardness, contamination, and grain size. - Hydrodynamic Conditions
– Current velocity, swell, tide cycles. - Disposal Strategy
– Reclamation, offshore dumping, geobags, or ponds. - Environmental Restrictions
– Turbidity limits, noise restrictions. - Production Targets & Deadlines
– Determines whether hydraulic or mechanical systems are ideal.
Our general industry insight:
CSDs and TSHDs dominate high-volume, time-sensitive projects, while backhoes and augers are winners in precision environments.
10. How Rock & Reef Delivers End-to-End Dredging & Marine Engineering Solutions
This is where your brand’s strength must shine.
Rock & Reef provides:
- Capital dredging
- Maintenance dredging
- Pipeline trenching & backfilling
- Rock dredging
- Land reclamation
- Shipbuilding services
- Custom marine engineering solutions
Your team’s advantage lies in operational reliability, fleet capability, in-house workshops, technical project planning, and safety-first execution.
11. Final Thoughts & Specialist Recommendation
Every dredger has a specific role. No single machine fits all terrains. The smartest move for any client is to align soil conditions, environmental guidelines, and production expectations with the right dredger type from day one.
If you’re planning a capital or maintenance dredging project anywhere in India, Rock & Reef can support you with technical evaluations, dredger deployment strategies, and complete marine engineering solutions.





